
Cost of Labor: This accounts for what you pay employees who work directly on creating your products (even if you purchase them from a manufacturer).Cost of Materials: The most direct cost in COGS, this includes the parts used to make your products (or source them from the manufacturer), raw materials, and items purchased for resale.Together, these two numbers give you an accurate picture of where you stand with inventory and COGS and, more importantly, where you stand on gross margin.”īut what costs actually go into calculating COGS? Here are some of the main costs associated with cost of goods: Then, your balance sheet should also show an inventory balance reflective of all the product you have remaining. “At the end of each month you should have revenue and COGS on your profit and loss statement reflective of the margin you enjoyed on those products at the time of their sale. What Numbers Make Up COGS?Īccounting firm Ledger Gurus give a fantastic explanation for the form and function of COGS. Since LIFO reflects current costs regardless of current inventory, LIFO results in a higher reported COGS.įor more detail on these four models for COGS, see our past posts on calculating costs of goods sold. Last-In, First-Out (LIFO): This model assumes you sell your newest inventory first.
FIFO will most closely match costs with your ending inventory on your balance sheet. First-In, First-Out (FIFO): This model takes a running aggregate view of COGS, assuming that you will both purchase and sell the same unit first.It’s the best model for high-value, unique or customized items you need to identify individually. Specific Identification Method: This takes a specific cost into account for each unit.Multiply the units sold by the average cost.
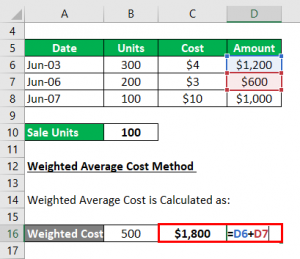
This model treats your inventory as a whole, and doesn’t take specific units into account. Weighted-Average Method: The average cost of all your units and inventory.In one of our previous posts, we discussed the different methods to calculate COGS for ecommerce: And with stiff price competition, comparison shopping and razor-thin margins, ecommerce brands must accurately model COGS (and other costs that affect profitability).
#COGS COST OF GOODS SOLD HOW TO#
Some companies that sell a mix of products and services prefer a broader term, cost of revenue, of which COGS is one component.To get the full value out of COGS, ecommerce companies need to know how to calculate it.

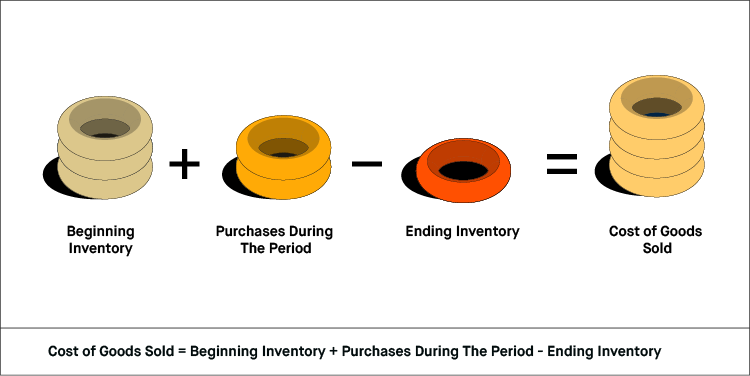
The gross profit can then be used to calculate the net income, which is the amount a business earns after subtracting all expenses.ĬOGS is sometimes referred to as cost of merchandise sold or cost of sales. This is the amount a business earns from sales before deducting taxes and other expenses. Once the cost of goods sold has been found, the answer can be used to calculate a business’s gross income. The cost of creating goods or services that are not sold should not be included.ĬOGS = Beginning Inventory + Purchases during the Period – Ending Inventory Costs can only be expensed and shown in the P&L after the goods have been sold and their revenues reported in the P&L. In accounting, COGS is a standard item in the expense section of a company's profit and loss statement (P&L). COGS includes direct costs, such as material and labor, but does not include indirect costs, such as sales, marketing or distribution. Cost of goods sold (COGS) is the total of the costs directly attributable to producing things that can be sold.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
